| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 임베디드타입
- Git
- embededtype
- OSIV
- springboot기본설정
- sql
- 에이치투데이터베이스
- Open EntityManager
- JPAproxy
- 자바제너릭
- 스프링부트기본설정
- javageneric
- httppie
- jpa
- jpqlquery
- spring
- dockercmd
- 이해와 원리
- 데이터베이트h2
- JDBC connection pool
- 스프링부트
- 제이피큐엘쿼리
- gitinitial
- JPA값타입
- JPAmapping
- springbootH2
- JPA Hint & Lock
- JPA프록시
- springbootproxy
- MySqlType
Archives
- Today
- Total
빡코
[토비_스프링부트] #3 DI와 테스트, 애노테이션 활용 본문

테스트 코드를 이용한 테스트
TestRestTemplate
package tobyspring.helloboot;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.http.*;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
public class HelloApiTest {
@Test
void helloApi() {
//http localhost:8080/hello?name=Spring
TestRestTemplate restTemplate = new TestRestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<String> res = restTemplate.getForEntity(
"http://localhost:8080/hello?name={name}", String.class, "Spring");
//검증 3가지
//status cod 200
assertThat(res.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
//header(content-type) text/plain
assertThat(res.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE)).startsWith(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE);
//body Hello Spring
assertThat(res.getBody()).isEqualTo("HelloSpring");
}
}
DI와 단위 테스트
컨테이너 없이 실행하는 단위 테스트
public class HelloControllerTest {
@Test
void helloController() {
//HelloController를 다른 오브젝트로부터 고립 시켜서 테스트
HelloController helloController = new HelloController( name -> name);
String ret = helloController.hello("test");
Assertions.assertThat(ret).isEqualTo("test");
}
@Test
void failsHelloController() {
HelloController helloController = new HelloController( name -> name);
//예외가 발생했음을 검증
Assertions.assertThatThrownBy(() -> {
String ret = helloController.hello(null);
}).isInstanceOf(IllegalArgumentException.class);
//공백 문자 체크
Assertions.assertThatThrownBy(() -> {
String ret = helloController.hello("");
}).isInstanceOf(IllegalArgumentException.class);
}
}public class HelloServiceTest {
@Test
void simpleHelloService() {
SimpleHelloService helloService = new SimpleHelloService();
String ret = helloService.sayHello("Test");
assertThat(ret).isEqualTo("Hello Test");
}
}public class HelloApiTest {
@Test
void helloApi() {
//http localhost:8080/hello?name=Spring
TestRestTemplate restTemplate = new TestRestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<String> res = restTemplate.getForEntity(
"http://localhost:8080/hello?name={name}", String.class, "Spring");
//검증 3가지
//status cod 200
assertThat(res.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
//header(content-type) text/plain
assertThat(res.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE)).startsWith(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE);
//body Hello Spring
assertThat(res.getBody()).isEqualTo("HelloSpring");
}
@Test
void failsHelloApi() {
//http localhost:8080/hello?name=Spring
TestRestTemplate restTemplate = new TestRestTemplate();
ResponseEntity<String> res = restTemplate.getForEntity(
"http://localhost:8080/hello?name=", String.class);
//검증 3가지
//status code 200
assertThat(res.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
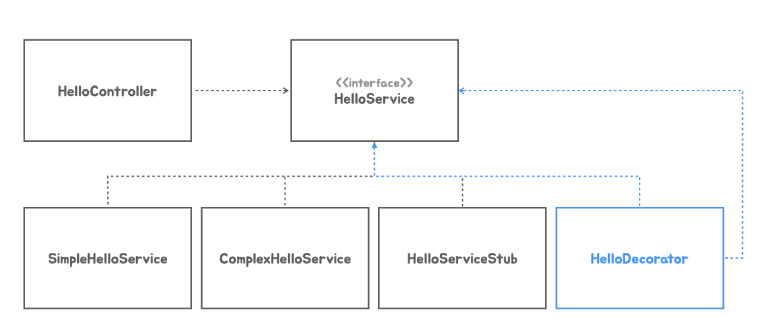
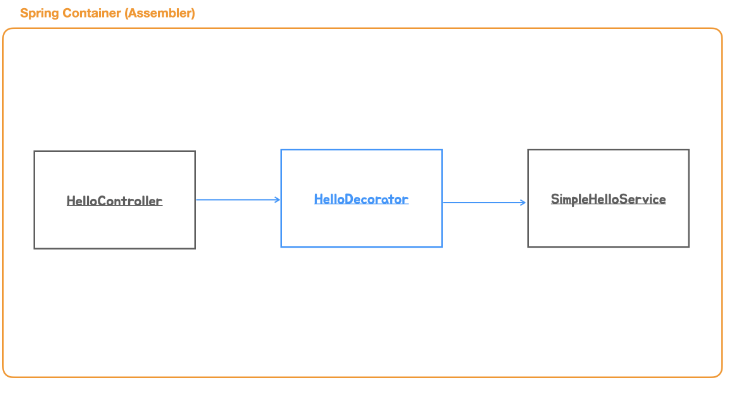
DI를 이용한 Decorator 패턴과 Proxy 패턴
Decorator Pattern
기존 코드에 동적으로 책임을 추가할 때 쓰는 패턴.
오브젝트 합성 구조로 확장이 가능하도록 설계되어있고 DI를 적용해서 의존관계를 런타임에 주입할 수 있다면 의존 오브젝트와 동일한 인터페이스를 구현한 확장기능(데코레이터)을 동적으로 추가할 수 있다. 재귀적인 구조로 여러 개의 책임을 부가하는 것도 가능하다

@Service
@Primary //우선 적용
public class HelloDecorator implements HelloService {
private final HelloService helloService;
public HelloDecorator(HelloService helloService) {
this.helloService = helloService;
}
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "*" +helloService.sayHello(name) + "*";
}
}
테스트
public class HelloServiceTest {
@Test
void helloDecorator() {
HelloDecorator decorator = new HelloDecorator(name -> name);
String ret = decorator.sayHello("Test");
assertThat(ret).isEqualTo("*Test*");
}
}
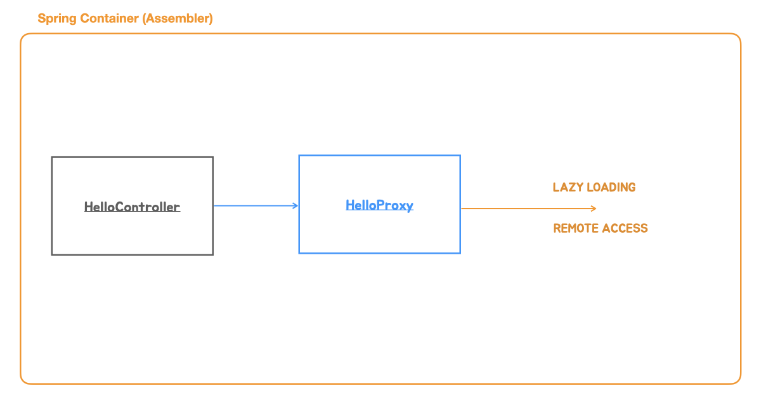
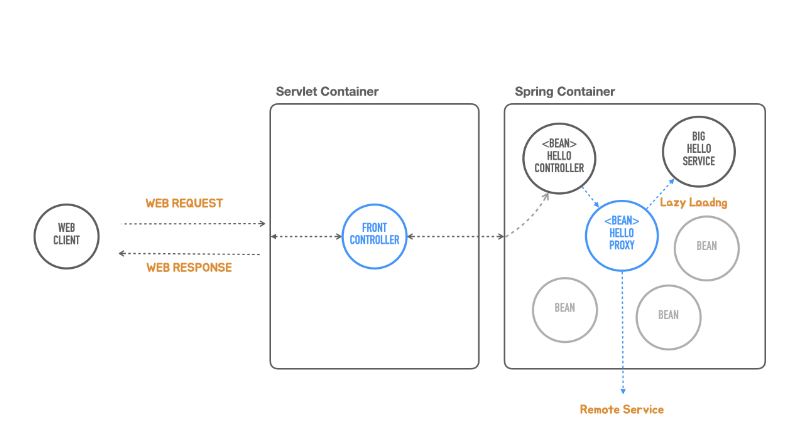
Proxy Pattern
프록시 패턴에서 프록시는 다른 오브젝트의 대리자 혹은 플레이스 홀더 역할을 한다. 프록시는 리모트 오브젝트에 대한 로컬 접근이 가능하게 하거나, 필요가 있을 때만 대상 오브젝트를 생성하는 필요가 있을 때 사용할 수 있다. 보안이나 접속 제어 등에 사용하기도 한다.
'Java > Spring-boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [스프링]스프링 컨테이너를 다루는 방법 (1) | 2023.12.27 |
|---|---|
| [스프링]스프링 컨테이너 (0) | 2023.12.27 |
| [스프링+DB]Spring에서 Database 접근하기 (0) | 2023.12.26 |
| [스프링부트] 프로젝트 초기 기본 설정 (0) | 2023.02.05 |
| 스프링부트_JPA_데이터베이스_에러 (0) | 2020.01.05 |



